A family budget template is an effective tool that helps you maintain financial stability and achieve your goals. You can use it to track and manage your household income and expenses. Every member of your family should be involved in creating a family budget.
Table of Contents
What is a family budget?
A family budget is a plan for your income (comes in) and expenses (goes out) over a specific period of time. This plan is a tool for empowering yourself. It is a way to allocate your income to specific things so that it works for you.
How to create a family budget that works?
Here are the pointers to create an effective family budget;
Start with estimates
Set aside time with your family members (you, your partner, your kids, and your parents who live with you) to start your budget. You need to ensure that every member should feel level-headed and up to the task. First, create transparency about where you are now.
Start with estimates and write down what you have in your savings and then move on to debts. Think about the balance for each of your loans. After that, estimate the rest of the spending such as the expenses you spend on groceries, clothes, utilities, etc. Keep in mind that this step involves just an overview of everything.
Get a baseline of your expenses
Take a short break when creating the family budget in order to avoid getting overwhelmed. After a break, go through your financial accounts and write down the actual amount that you had estimated. This point enables you to determine a couple of ways to adjust your family finances.
Moreover, identify the areas where you can reduce or eliminate specific expenses. Consider relocating those expenses to be more in line with your goals. At this point, you have a better understanding of where your family’s income is going. Now, you can easily start budgeting as you have a baseline of your savings, debts, and expenses.
Start budgeting
You have to be clear on how much money is coming in and where your money is going. You can start with a 50/30/20 budgeting method. It divides your income into three ways;
- 50% towards needs (basic utilities, transportation, housing, groceries, and more)
- 30% towards wants (travel, gifts, and meal out)
- 20% towards savings (emergency funds, retirement, etc.)
The 50/30/20 method is just one way to plan for your money. You can also use different budgeting systems that vary in rigidity and goals.
Consider using a worksheet or app
You can also use a tool such as a budget spreadsheet to enter every household expense. Next, indicate how your spending aligns with the 50/30/20 budgeting method. In addition, you can use free budget spreadsheets from Microsoft Office, Google Drive, and other websites. These tools enable you and your partner to reference each other’s spending and saving details.
You need to select the tool that you can use very comfortably. If you aren’t interested in entering your expenses daily then use a tool that tracks the spending for you.
Keep budgeting
You need to adjust the budget often specifically if you have dependents whose expenses change over time. Continually checking on the budget with your household is more important than getting it right. Therefore, schedule budget reviews daily. Note down the following when you check in;
- How your spending has changed
- Discuss what you may need to do differently to go forward
- Plan for upcoming expenses
Another important thing to plan for your money and keep at it is to communicate about your individual goals and family goals.
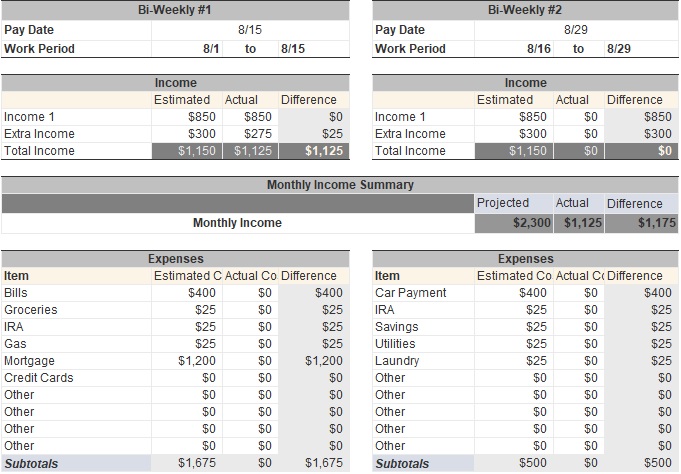
Bi-Weekly Family Budget Template
Family Budget Worksheet Example
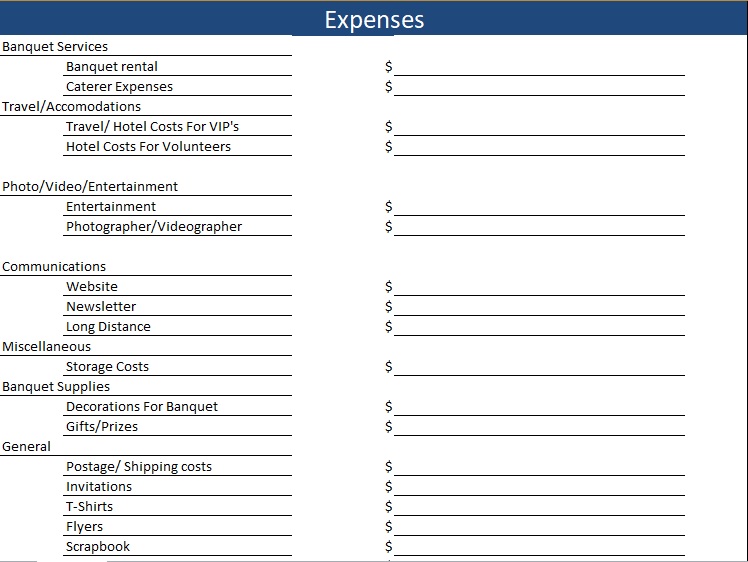
Family Reunion Budget Worksheet Template
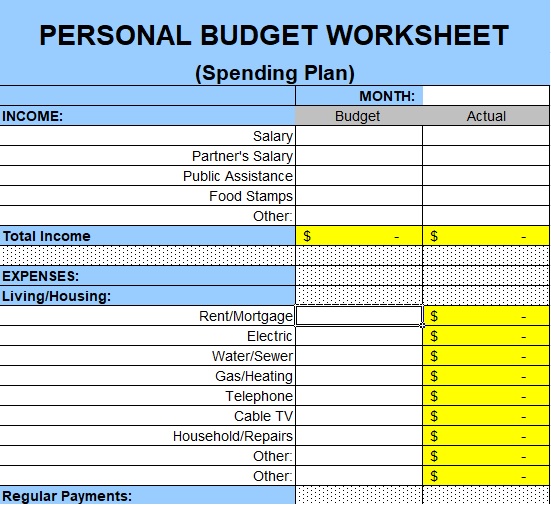
Best Family Budget Template
Family Financial Planning Template
Family Budget Worksheet Excel
Family Budget Calculator Template
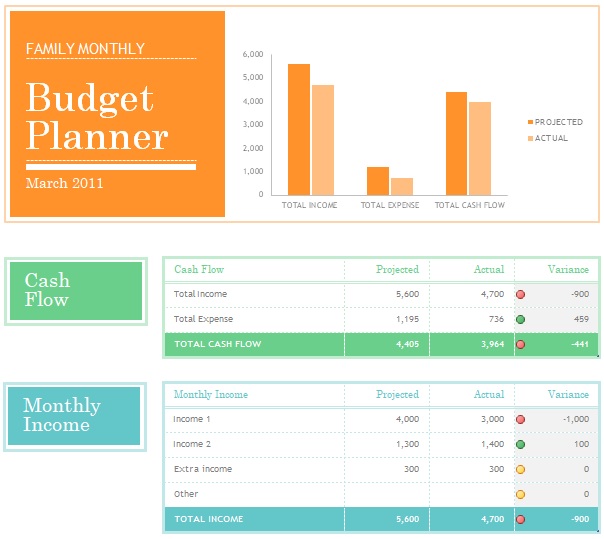
Monthly Family Budget Template
FAQ’s
There are three types of family budgets;
1- Deficit budget (the expenditure exceeds the income)
2- Surplus budget (the income is more than the expenditure)
3- Balanced budget (a good budget)
The basic family budget includes the following items;
1- Housing
2- Food
3- Child care
4- Transportation
5- Health care
6- Other necessities
7- Taxes