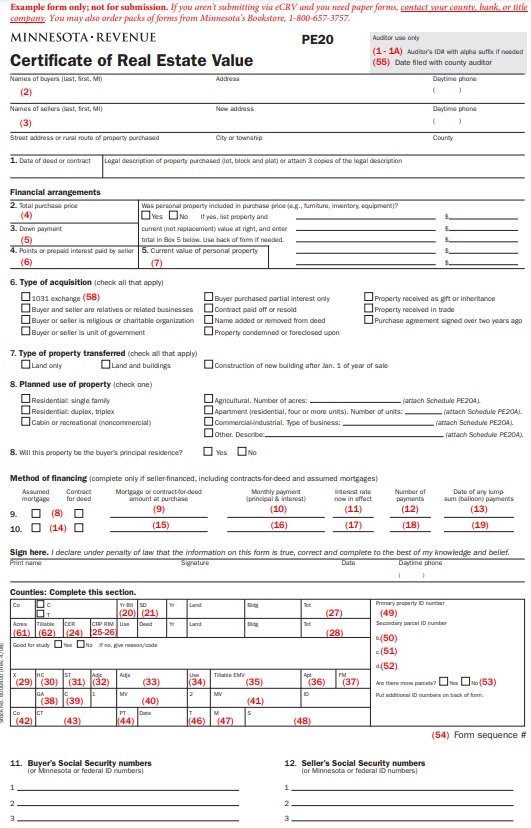
A contract for deed template is a legal document that specifies a seller-financed real estate purchase. This document comes in handy when selling different real estate property types such as residential, commercial, or raw land.
Table of Contents
What is a contract for deed?
A contract for deed is a written agreement between a buyer and a seller stating that the buyer will pay the seller in installments for a piece of real estate they have purchased. The seller plays the role of the financial provider in this agreement. When the buyer has paid in full, the legal title of the property is transferred to the buyer.
When the buyer isn’t able to get a mortgage through a bank or other lending institution, they can pay the seller directly instead of qualifying for a mortgage. Some other names for contract for deed are;
- Land contracts
- Installment land contract
- Bond for deed
How does a contract for deed work?
A contract for deed is generally a legal agreement between a buyer and a seller but it can involve various parties in a real estate transaction. Unlike a mortgage, this document doesn’t require a third-party lender like a bank or another financial institution. Moreover, both the buyer and the seller must agree upon key contract elements in order to establish a legally binding Contract for Deed.
After executing the contract, the buyer starts paying the monthly installments to the seller as per their agreed-upon schedule. The seller has the property’s legal title in their name during this period while the buyer has the equitable title. At any time, the buyer can allow to make lump-sum payments on the balance. However, it depends on the agreed-upon terms.
The seller must transfer the legal title to the buyer when they have received the total purchase price. Also, every state has different laws regarding contract for deed so you must understand your state’s laws before executing your agreement.
What to include in a contract for deed?
Your contact for deed must include the following key elements;
Purchase price
The contract for deed can’t be binding without a mutually agreed-upon purchase price.
Payment plan
After negotiating a purchase price, the buyer and the seller must decide on a payment plan that may include a down payment. This document allows the buyer to provide a smaller down payment. Furthermore, the agreement also specifies the following details;
- The amount of each monthly payment
- The first payment due date
- The specific day of the month on which all consecutive payments are due
Interest rate
Specify in the contract whether or not the seller is charging interest. The seller may not charge interest if they have a close relationship with the buyer. However, it would be better for the seller that before setting an interest rate consult their jurisdiction’s usury laws about interest rate limitations.
Default protocol and penalties
If the buyer breaches the agreement or fails to make timely payments, they default. The seller must specify in the agreement that the buyer has to pay a fee for late payments and when the buyer has to leave the property if the agreement is terminated.
Rights and obligations
In the agreement, it is important to make it clear which party is responsible for property taxes and insurance. Also, state that the buyer cannot transfer the purchase to another party, and when the total purchase price is paid, the seller is obliged to transfer the property title.
contract for deed template
financing addendum for contract for deed
house contract for deed form
land contract for deed form
standard land purchase and sale agreement
real estate contract for deed form
FAQ’s:
What are the rights of the buyer in a contract for deed?
Here are the key rights of the buyer;
- Equitable title
- Control over property
- Default grace period
- Option to purchase
- Right to recession
- Fair treatment
- Right to legal representation
What is the difference between a contract for deed and a mortgage?
A contract for deed is a legal agreement between a buyer and a seller in which the buyer has the equitable title. On the other hand, a mortgage is an agreement between a buyer and a third-party lender (a bank or private lender) in which the buyer has the legal title.